Blog
Our blog provides readers an opportunity to hear from the Advance Illinois staff and partners on education policy issues affecting Illinois students and beyond.
The Importance of Statewide Kindergarten Readiness Data in Supporting Early Childhood in Illinois
Overview
To make informed policy decisions and direct resources where young children and their families need them most, Illinois needs comprehensive and robust statewide data. A key piece of that data is understanding kindergarten readiness as children enter formal schooling. Having a developmentally appropriate way to understand where our youngest learners are across important domains helps provide a window into how ready new students are to learn and grow as they begin their school journey. In turn, this allows the state to plan and allocate investments and resources.
The Illinois State Board of Education’s (ISBE) recently released the 2025 Illinois Report Card, including the 2024-2025 Kindergarten Individual Development Survey (KIDS) data. While districts may have other information and data to assess kindergarten readiness, KIDS is currently the only comparable statewide data we have available to help us understand kindergarten readiness across Illinois.
2024-2025 KIDS Data
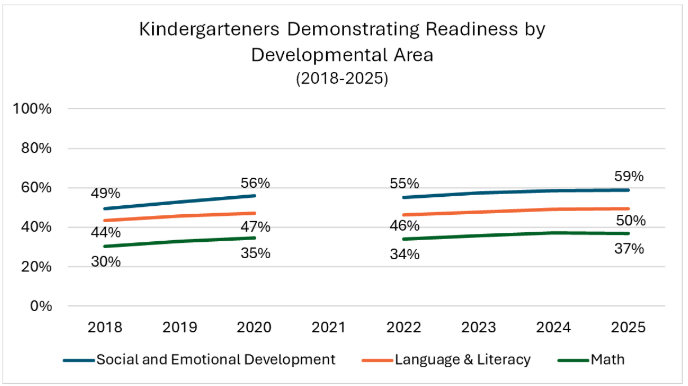
KIDS assesses students on 14 measures across three domains: language and literacy, math, and social emotional development.
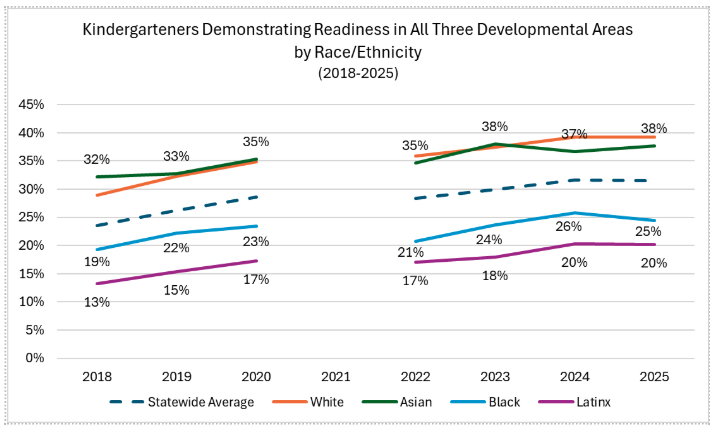
In SY24-25, 31.5% of kindergartners demonstrated readiness in all three developmental areas, holding fairly steady to the prior year and contributing to an arc of steady growth over the 7-year stretch (with the exception of SY21, that was impacted by the pandemic). More youngsters demonstrated readiness for kindergarten in social & emotional development, while just under half were ready in language and literacy development, and just over one-third were on track for math development.
Although there were no major shifts this past year, the data continues to reveal disparities in kindergarten readiness across demographic groups.
More specifically, KIDS data reveals that gaps across lines of race, income, and learning style begin before children begin formal schooling, emphasizing the need for investments in high-quality early childhood care, services, and education that prioritizes children most in need.
While kindergarten readiness rates dropped across English Learners, children with IEPs, children receiving free or reduced lunch, and children who are homeless in SY24-25, kindergartners from low-income households (FRPL) experienced the most significant drop, declining by 1 full percentage point.*
That being said, although kindergarten readiness rates declined modestly across various student groups last year, the overall level of readiness has improved by more than 8 percentage points since the state first began observing incoming students in 2017. And it is good news that overall readiness for students receiving FRPL has grown by 6 percentage points.
Concerns about the Drop-Off in Response Rate
One area of concern about this year’s KIDS data is the drop-off in the number of children being observed. The percentage of kindergartners observed and assessed decreased statewide for the first time since the pandemic, dropping from 90.9% in SY2023-2024 to 87.1% in SY2024-2025. Among other things, this makes direct comparisons between years more difficult, particularly for the Chicago Public Schools (CPS), where the percentage of kindergartners observed dropped more dramatically from 88% to 73.3% in a single year.
For statewide data to be valid and useful, participation rates need to be high. Importantly, training and coaching help teachers successfully implement this observational tool and so we hope and trust the state will continue to invest in these strategies. In addition to ensuring more accurate information, training and coaching strengthen skills with broader classroom value.
Conclusion
While it is good news that the number of students demonstrating kindergarten readiness has been steadily increasing, the sad fact is that overall rates of readiness across the state remain lower than anyone would like, with just a third of kindergarteners demonstrating readiness in all three assessed developmental areas. This speaks powerfully to the need for significant investment in high-quality early learning and care. As importantly, the persistent gaps that emerge even before children reach kindergarten highlight the need to make equitable investments across the early childhood service spectrum, including in early intervention for very young children with developmental delays and disabilities.
Having statewide data on kindergarten readiness that is comparable across districts is essential for ensuring we understand the overall and more targeted needs facing families and communities. From there, it is up to us to make sure we put that knowledge to work.
—-
*(The data on English Learner kindergarten readiness should be cautiously interpreted given that alternative language assessments are not systematically used across districts. IWERC, Trends and Disparities in Readiness Using KIDS, 2024.)
Kate Buchanan is the Senior Policy Advisor, Early Childhood for Advance Illinois.
Kindergarten Readiness and What's Next for KIDS
As part of the Illinois State Board of Education’s (ISBE) recently released Illinois Report Card, the state included the 2023-2024 Kindergarten Individual Development Survey (KIDS) data.
Since the tool’s statewide implementation in 2017, KIDS data has been the state’s window into understanding kindergarten readiness among Illinois children in a developmentally appropriate way. While KIDS is not the only student outcomes data available at the local level, it is the one and only data we have at the state-level to understand readiness across districts. The data has been eye-opening and has both motivated and enabled district and statewide policymakers to make data-driven decisions that support systems and programs improving kindergarten readiness.
The data reveals that in the 2023-2024 school year, 31.6% of all students in Illinois demonstrated kindergarten readiness in all three developmental areas (social and emotional development, language and literacy development, and math), a slight improvement from the previous year. While it is good news that the state has shown some improvement in overall readiness, it is disturbing to know that gaps across lines of race, income, and specialized learning style not only begin before young learners enter kindergarten, but that these gaps remain stubbornly persistent.
Percentage of Readiness in all Three Developmental Areas by Race/Ethnicity, 2017-2024
Percentage of Readiness in all Three Developmental Areas by Student Group, 2023-2024
Why KIDS Data Matters
Findings from a series of recent reports from the Illinois Workforce and Education Research Collaborative (IWERC) on Kindergarten readiness are consistent with what the latest KIDS data reveals about disparities between student groups. White and Asian students were 15 to 25 percentage points more likely than Black and Latinx students to be kindergarten ready in all three domains. Students who were eligible for Free or Reduced-Price Lunch (FRPL), were English Learners (ELs), or had an Individualized Education Program (IEP) were 15 to 25 percentage points less likely to be kindergarten ready in each of the three domains. Report authors go on to answer a critical question in their secondary report: do disparities grow, shrink, or remain stable as students move through the educational system? The answer - kindergarten readiness predicts later academic achievement. Specifically, students who enter kindergarten with demonstrated readiness are more than twice as likely to be proficient in Math and English Arts in Grade 3. That relationship affirms the relevance of the tool, but here are a few things to consider.
Readiness on KIDS alone does not guarantee later academic success. Data indicates that Black, Latinx, and those students who receive free/reduced price lunch are less likely to score at or above proficiency in Grade 3. These trends are particularly troublesome, underscoring the need for targeted supports (e.g. technical assistance, increased resources) during the early and primary years, further consideration of the mixed-delivery system, and better understanding of individual family needs.
In addition, while it is understandable that there is a relationship between kindergarten readiness and later academic proficiency, the truth is, our goal should be to disrupt that relationship. Put differently, when KIDS data lets us know that a student may be struggling, it creates an opportunity for us to provide the support necessary to catch the child up. If we are able to do that effectively, one would hope that later academic proficiency would consistently exceed kindergarten readiness levels.
What is the State Doing to Support KIDS
Over the last few years, with support from the McCormick Foundation, the Illinois State Board of Education (ISBE) has hosted annual KIDS Summits. At the November 2024 KIDS Summit, over 200 teachers, districts, and school administrators convened to learn from experts and peers across the state about various applications of the tool’s data, guidelines of the tool’s implementation for special populations, and connections of KIDS to the Illinois Comprehensive Literacy Plan. This year’s main topic was meeting learning standards through play with other sessions ranging from using play for learning and assessment in special education settings to the role of play-based learning in the transition from PreK to K. The clear takeaway from the summit was that a play-based learning environment is essential to achieving KIDS' full potential in kindergarten classrooms and critical in understanding where children are developmentally in their learning journey. Beyond the tool’s implementation, there has been a false dichotomy between play and learning when in fact they are seamlessly intertwined, and play-based learning has proven to be critical to students’ learning and development.
How KIDS Can Improve
While we were excited to see ISBE prioritize play-based learning in this year’s summit, more can be done to not only improve the tool’s implementation, but also to support a statewide focus on closing outcome gaps between student groups for our youngest learners. The KIDS Advisory Committee has recommended that ISBE address these issues through increased community engagement with district leaders to better understand the tool’s current administration and application. The feedback can then be used to create materials that details how KIDS can assist districts in strengthening their K-2 instruction. Lastly, ISBE should consider increasing the number of measures that are required for KIDS. Evidence from current districts who administer the tool with increased measures suggest that if the KIDS tool is administered more than the required number of measures across multiple times in the school year, educators can make better use of the data to inform and advance developmentally appropriate instruction.
What’s Next?
Following the momentum of the successful KIDS summit, the recently released KIDS data, and the IWERC KIDS reports, we look to ISBE to provide strategies that put the state on the path to fulfill the goals and design of KIDS for all students, including those who are diverse learners and English Learners. With the state’s new Illinois Department of Early Childhood (IDEC) in its first planning year, it is a critical time to examine persistent gaps in kindergarten readiness and ask ourselves how we can do better to fulfill the needs of our youngest learners. IDEC, in partnership with ISBE and other stakeholders, has the unique opportunity to 1) use the data we already have to inform the development of stronger and more equitable systems that lead to closing readiness gaps and sufficiently preparing young children from birth to age 5 for kindergarten while also 2) practicing active continuous improvement of the current KIDS assessment and system to improve data reliability and validity.
Maya Portillo is the Senior Policy Advisor for Advance Illinois. Melissa Maldonado is a Policy Analyst for Start Early.