From the Desk
Our From the Desk publications serve as an avenue for us to discuss in-depth education policy issues that we support.
From the Desk—In the Face of Uncertainty, Working Together for Illinois Students and Children
I struggled with how to begin this end-of-year reflection. Like most of you, I am looking forward to taking time with my family as we celebrate the holidays and look ahead to a New Year. But it is hard to know quite what to say about a year that contained such unprecedented change and uncertainty, let alone one that included so much hardship and that is closing with such tragic headlines.
Months of federal actions are changing the landscape of public education. While certainly there was (and remains) room to improve the way in which we operate sprawling and significant federal programs, most changes go far beyond reform. Instead, many undermine decades of hard-won work to safeguard, improve, and expand access to opportunities for millions of children and students in this country who rely on our public schools, as well as programs that ensure families have food and medical care. And while a new administration inevitably brings with it changes in funding priorities, there are forward-looking processes for that change – ones that allow programs and their participants to plan and adjust without causing disruption and harm. In a departure from all norms and legalities, that is not what happened this year.
2025 has brought with it:
Vigorous executive branch efforts to dismantle the Department of Education, notably by dramatic reductions in staff that are causing delays in critical payments and programs, and with an outsized impact on data collection, civil rights enforcement, special education and federal student financial aid programs.
Cancellation or pausing of nearly $900M in research contracts that weaken stakeholder ability to make informed decisions to strengthen practice and policy and, by extension, student achievement.
Punitive demands on institutions of higher education, with critical federal funding threatened or withheld to ensure compliance with demands that exceed (and in some cases pervert) civil rights laws.
Funding that was by turn frozen (then released), rescinded, or delayed – often with little or no notice or process, and outside the normal budgeting process.
Deployment of immigration enforcement officials (and those hastily deputized) to conduct aggressive operations in Illinois and elsewhere that produced little success, by the agency’s own objectives, but sowed fear and loss in communities that spread far beyond the immigrant communities it targeted.
I could go on.
Instead, I will turn to the positive. Despite the issues generated by federal upheaval, Illinois accomplished some important work for children and students:
Protecting Public Spaces of Learning and Care
In the face of aggressive immigration and law enforcement efforts led by the federal administration in states across the country, including our own, the General Assembly passed, and Gov. Pritzker signed, a series of state laws aimed at protecting immigrant and newcomer children, students, and families in public education settings from unlawful immigration enforcement activities. The Safe Schools for All Act (HB3247) codified constitutional law and protects the rights of all students to access public k-12 education regardless of their immigration status. Among other things, the law prohibits schools and districts from disclosing or threatening to disclose the actual or perceived immigration status of students or their caregivers. Further, HB1312, passed in veto session, places similar restrictions on child care staff as well as public colleges and universities, both of which will be prohibited from disclosing citizenship information about students or employees. Children cannot be expected to learn– let alone attend school - if they do not feel safe. Districts including Chicago Public Schools have in fact reported concerning drops in attendance amid ICE raids in the Chicago area, so we applaud lead bill sponsor State Senator Karina Villa and the Latino Policy Forum, Illinois Coalition for Immigrant and Refugee Rights (ICIRR), Mexican American Legal Defense and Educational Fund (MALDEF), The Network: Advocating Against Domestic Violence, Legal Action Chicago, the Law Office of the Cook County Public Defender, Start Early, Illinois Action for Children, and many other advocates for championing this important legislation that enshrines Illinois’ protection for every child and student and their family to learn without fear.
Supporting Student Well-being and Mental Health
As our own State We’re In: 2025 reveals, mental health issues continue to impact student achievement. Chronic absenteeism here and nationally remains at worrisome and high levels, and students continue to report elevated levels of depression and suicidal thoughts. Appropriately, the state advanced efforts to understand and support child well-being and mental health, which are fundamental to learning and growth. Among other things, ISBE released the Children’s Adversity Index in June, which identifies where and to what degree community level trauma is present across the state, putting powerful data into the hands of advocates and lawmakers alike to expand and target resources to foster safer, healthier school communities. In addition, during this past legislative session, state lawmakers passed SB1560 requiring all schools to offer voluntary mental health screenings to students enrolled in grades 3 through 12, at least once a year, beginning with 2027-2028 school year. And to address ongoing attendance issues (which remain one of the most powerful indicators of academic success), the General Assembly created a Chronic Absence Task Force to develop recommendations and report on progress. Finally, at the collegiate level, HB3385 requires all institutions to provide licensed clinical counselors, social workers, or other mental health professionals on campus. With more tools capturing greater insight into student mental health and community conditions, and more mental health personnel being deployed on college campuses, Illinois is setting the stage for healthier schools and more data-driven decision making to sustain them.
Establishing Key Systems for Transparency and Accountability
This year, the state was successful in paving a path for more data-driven decision- making, and greater equity and access at both the early childhood and postsecondary levels. SB0406 creates a new Early Childhood Integrated Data System (ECIDS) to collect, integrate, store and report on early childhood data across programs and agencies. While it will take time for ECIDS to be up and running, it is badly overdue and will help anchor critical work going forward allowing the agency to develop tools for parents and communities to access aggregated data On the other end of the education spectrum, SB2039 calls for a new public-facing and centralized higher education dashboard to report on everything from institutional affordability to student enrollment, persistence, and completion, starting in 2027. These developments strengthen the state’s education data infrastructure and transparency, and they could not come at a more urgent time, as federal actions have slashed data and research support and infrastructure.
Making sure that all children have what they need to live up to their full potential remains one of the most important responsibilities we all have. It is both the right thing to do, and it is the surest way to strengthen the future for all of us. The United States was among the first in the world to recognize the importance of educating every young person and to invest (however imperfectly) in public education for all. Leaders of every political stripe have understood and championed the value of strong public schools, not just to ensure economic and political vitality, but to forge civic and community relationships. And Americans from every corner of the country have consistently reaffirmed the value of meeting children where they are.
As we head into 2026, I hope that these strong and common values will ensure that we continue to not only invest in the next generation, but that we do so with the understanding that we all benefit when everyone has the chance to learn and grow.
So let us recommit ourselves to focusing on the next generation; on what they need to succeed. And let us take time this holiday season to appreciate those who support our young people in classrooms and childcare centers and college campuses. Let us rest and rejuvenate with family and friends…then come back together to make a positive difference in the New Year.
Warmly,
Robin
From the Desk—Reflecting on the Lasting Impact of How Adults Show Up
Research and common sense tell us that psychological safety plays a powerful role in an individual’s ability to take risks, to express themselves, to make mistakes, and to be vulnerable – all activities critical to the learning process. And we likely need no research to remind us that emotional and physical safety are essential to well-being. So it is heartbreaking to witness the social, emotional, and physical harm being caused by aggressive and increasingly violent ICE activities and the National Guard deployment here in Illinois. It is hard to conceive how anyone – regardless of political party or position on immigration issues – could not be appalled by the inhumane enforcement on display; to be horrified to see federal agents terrorize families by raiding homes and shelters in the dead of night, or separating parents from their children; to be alarmed at the sight of armed agents on train platforms and outside early childhood centers, schools and colleges; to be baffled by decisions to uproot hard-working and law-abiding people who are actively contributing to their communities with such callous disregard; and ultimately, to despair as many families forego education, health care, religious fellowship, employment, and more, for fear they will be profiled and targeted.
Sadly, children are no strangers to being fearful going to school, leaving school, and even while at school. We have a great deal of work to do to ensure safe families, schools and communities in every corner of our state and country. However, we count on our elected officials and our systems of government to improve things – to work to address the sources of trauma and fear, not to cause them. And make no mistake, whatever the justification for these actions, the impact of this ICE activity is being felt by all who have a friend, a colleague, a classmate, or a neighbor being targeted.
Advance Illinois does not work in the immigration policy space, and we do not pretend to know the best measures this country can and should take to balance the range of competing interests relating to immigration policy. But we know schools, and we work closely with communities across the state. We recognize the foundational role that safe communities play in anchoring learning and growth, and would ask leaders of every political stripe to work to advance policies and actions that enhance that safety and sense of well-being and eschew strategies that favor brute force at the expense of humanity.
In the meantime, we thank the families, educators, school and institutional leaders, superintendents, elected officials, and community partners and volunteers who are extending themselves to support and protect their students, colleagues, and neighbors. It matters how we show up. We hope our federal leaders reconsider their actions. Children across every demographic and immigration status are not only being harmed, they are also watching. One can only wonder and worry what they are learning.
—
RESOURCES
Illinois Immigration Information: This comprehensive, all-in-one resource hub is designed to help Illinois communities understand their rights and access essential services, including housing assistance, food programs, and more.
ACLU Illinois - Know Your Rights: Federal Forces Being Sent to Chicago: This resource offers updates on the presence of federal forces and the National Guard and includes “Know Your Rights” guidance to help community members safely engage as a witness or ally.
From the Desk— Remembering Governor Edgar, A Powerful Illinois Leader
In addition to serving Illinois as a principled, compassionate elected official, Gov. Jim Edgar served as Founding Co-Chair and champion of Advance Illinois and the bipartisan work it represents to strengthen educational opportunities and outcomes for Illinois students.
It is with heavy hearts that we write to honor the passing of former Governor Jim Edgar. At a time when political strife is on the rise, Illinois has lost a public servant who believed in public service and in using elective office to bring people together to improve the lives of all families. It is not surprising that Gov. Edgar remains one of the most beloved former governors in the state, or that he leaves a tangible, bipartisan legacy.
While in office, Gov. Edgar tackled thorny issues ranging from ballooning pension debt, and state deficits, to inequitable school funding, and did so while retaining broad-based support. After stepping down as Governor, Jim Edgar resisted calls to run for other offices, choosing instead to speak candidly about political issues and races, and to focus on mentoring the next generation.
In that vein, Gov. Edgar lent his considerable reputation and energy to founding two bipartisan organizations. First, he joined a group of civic leaders who came together to investigate whether and how Illinois could make more significant progress ensuring that every Illinois student had the education they needed to thrive and succeed. The group concluded that Illinois would benefit from an organization that worked on systemic issues and did so across traditional geographic, political, and other divides. Gov. Jim Edgar believed enough in the mission that he agreed to become founding co-chair of Advance Illinois. Partnering with Bill Daley, a well-known Chicago Democrat, Gov. Edgar lent his voice to establishing Advance Illinois as a credible, bipartisan organization committed to using data and research to identify high-impact strategies, and to working across the diversity of Illinois to engage and involve stakeholders.
Several years later, in a similar vein, Gov. Edgar founded the Edgar Fellows Program at the University of Illinois. The program has a simple, but important, goal: to bring the next generation of state leaders together to learn from and with each other about the issues the state faces. Explicitly, the goal was to ensure that every cohort of Edgar Fellows represented the political, geographic, gender, racial, and civic diversity of the state – with a special emphasis on leaders in or likely to pursue elected office. From there, the objective was for Fellows to get to know each other – well enough to work across divides on hard issues. The program boasts over 500 graduates and continues today.
As anyone who had the pleasure of working with him will attest, in addition to being a laudable public figure, Jim Edgar was just a wonderful human being. He was unfailingly candid, perceptive, engaging, and warm. At one of his final public appearances, he used his time to lament the importance – and absence – of compassion as a driving force in government. And that basic humanity was just as present up close. It will forever be a personal and professional highlight to have had the opportunity to work closely with Gov. Edgar in launching Advance Illinois. He spent untold hours with me discussing issues of the day, strategizing, or just reflecting on the world – hours filled with real interest in advancing good policy, a keen and self-deprecating sense of humor, and a genuine desire to support others to learn and grow. Jim Edgar cared deeply about Illinois and dedicated himself to finding ways to support its ongoing growth and health – through public service, through education, and through supporting the next generation of leaders.
I know we are not alone in mourning the loss of Governor Edgar. We join an extensive cross-section of the state in sending our condolences to his family and celebrating his legacy. We are grateful for who Gov. Edgar was, and, in turn, what he meant to our organization. Like others, we are committed to carrying on his legacy; to reach across divides to make great things happen for every child and student in our state.
From the Desk—What the Reconciliation Bill Means for Illinois Children, Families, Schools and Communities
On July 4, President Trump signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBB), a piece of federal spending legislation that makes significant changes to Medicaid, SNAP, and federal college loan and scholarship programs, the impact of which will be felt in the short term—as is the case with student loan disbursement and repayment conditions—as well as in the long term — like with Medicaid cutbacks, whose impact will unfold over time.
Below, we offer some explanations of the changes and their implications for schools and the students, families, and communities they serve, along with links to additional materials and in-depth coverage.
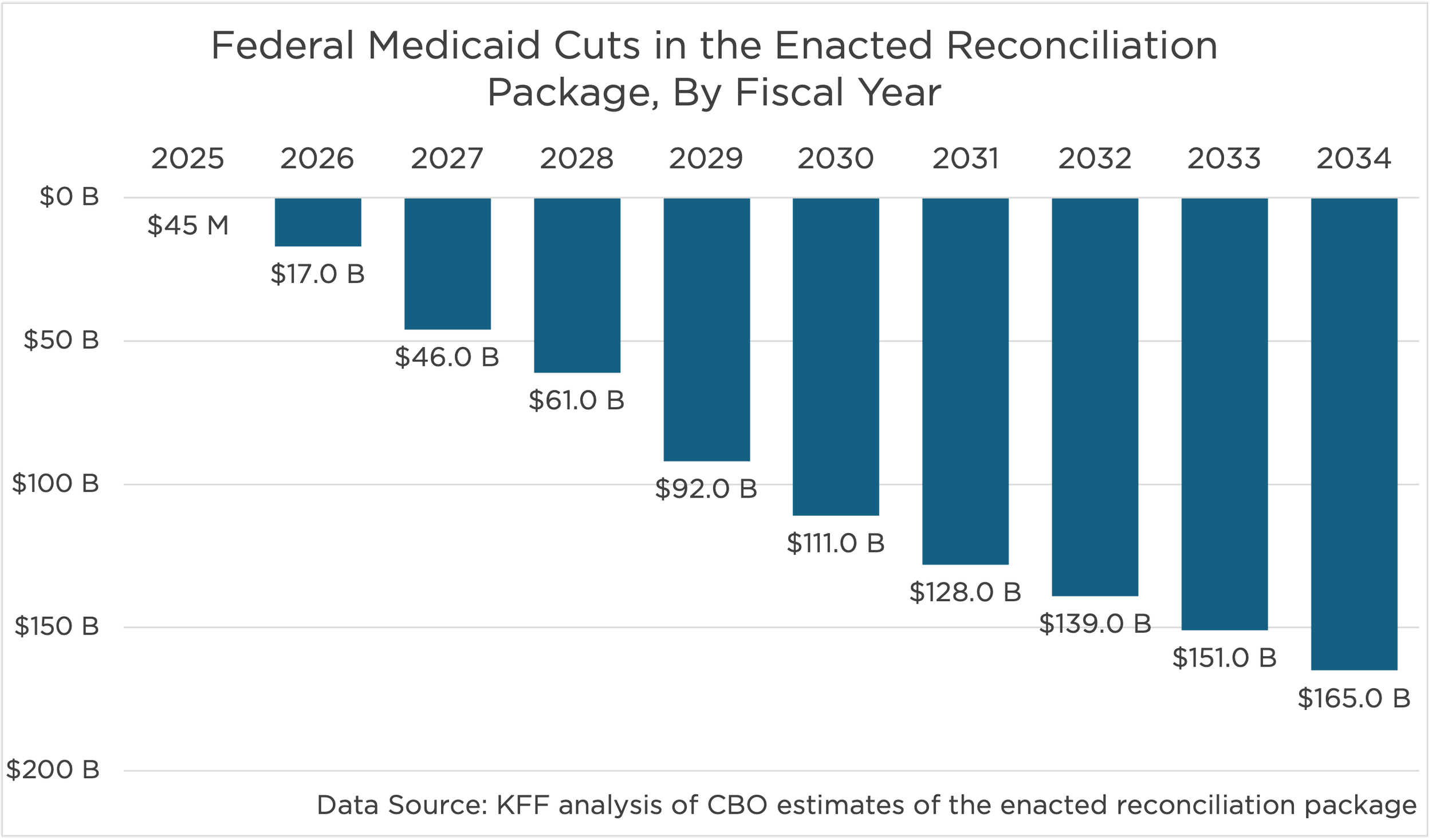
First, let’s take a look at how OBBB will impact Medicaid access. Over the past 10-15 years, the federal government has worked, largely consistently, to expand access to Medicaid, to make it easier for families to apply, and to simplify schools’ ability to seek reimbursement for medical care provided at or through schools. In an effort to cut costs, the current administration proposed, and OBBB codified, a series of changes to Medicaid they claim will save $911 billion over the next 10 years.
I imagine it’s obvious to even a casual observer and average math student, that the only way to save $911 billion is to reduce the number of people being served by Medicaid. In fact, experts from the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office estimate that the changes now underway could result in more than 10 million Americans losing coverage over the next 10 years; including anywhere from 270,000 to 500,000 in Illinois alone. Here are some of the key changes:
OBBB imposes significant new work requirements — something that previous administrations had deliberately avoided — in an effort to expand medical coverage. Data suggests that work requirements can in fact save federal dollars, but a pilot program in Georgia revealed that savings derive largely from under-enrollment. That is, the additional complexity created by understanding, complying, and verifying eligibility resulted in just 7,500 of roughly 240,000 eligible Georgia citizens receiving coverage. Worse, the increased paperwork requirements drove costs of enrollment up from an expected $2,490/participant to over $13,000/participant. Notably, a similar work requirement program in Arkansas did not meaningfully increase employment.
OBBB adds significant new reporting and verification steps, including requiring participants to verify eligibility every 6 months instead of annually, a change that both depletes time parents can spend with their children and likely will result in people losing coverage for reasons having nothing to do with need.
OBBB rescinds eligibility for a significant number of lawful immigrants. Specifically, the bill revokes access for refugees, individuals granted parole for at least one year, individuals granted asylum or related relief, certain abused spouses and children, and certain victims of trafficking. This is a devastating blow to vulnerable populations. Only some lawful immigrants maintain access to Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) under the new law: lawful permanent residents, certain Cuban and Haitian immigrants, and COFA migrants. Children and pregnant adults may still qualify through the Immigrant Children’s Health Improvement Act (ICHIA) only if the state they reside in opts into ICHIA. This provision goes into effect October 1st, 2026.
You may be wondering what this means for schools and their communities across Illinois. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Schools can get reimbursed for various health services provided to students who are enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP programs, and limits on eligibility will impact schools’ abilities to provide these services. Medicaid reimbursements are often used on telehealth, contracted services for mental and/or behavioral health, technology, care coordination and referral services, and Medicaid outreach and enrollment services. These reimbursements allow schools to provide crucial services to children where they spend most of their time—schools. As students lose access to Medicaid and CHIP, schools’ ability to fund important services will be impacted, leaving many students vulnerable.
Multiple analyses suggest that rural hospitals will be at greater risk of closing. Why? Rural hospitals serve a large number of Medicaid patients. As those patients lose coverage, the hospitals that serve them will lose reimbursements and/or patient load. Analysts looked at caseloads and prior financial margins to determine which rural hospitals, nationally, will be at risk for closure due to provisions in OBBB. The results identified over 300 rural hospitals across the nation at risk of closure, conversion, or service reductions — severely impacting the communities that rely on them. 9 of these rural hospitals are in Illinois; 5 of the 9 hospitals at risk are top Medicaid providers, and the other 4 have struggled financially.
Additional Ripple Effect: Should these hospitals close, clinics and primary care providers who depend on them will also be impacted and/or close. Taken together, the likely impact of Medicaid changes in OBBB will be to limit the services accessible to rural communities, pushing families to travel greater distances for healthcare, or lose out entirely.
Special Note: In response to concerns about rural hospitals potentially being forced to close, the final version of the bill creates a special grant program designed to shore up rural hospitals. This will hopefully help institutions withstand additional financial pressure, though it seems worth pointing out that the money set aside for this pot — $50 billion — will no longer get to hospitals by way of providing care for ailing rural residents.
Next, let’s take a look at how OBBB will affect SNAP. SNAP, or the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, is a federal program that helps low- and no-income people purchase food. Here, too, OBBB seeks to save money by cutting access to this 86-year-old program.
OBBB rescinds eligibility for a range of legal immigrants. The same groups of legal immigrants who are losing qualified status for Medicaid will also lose qualified status for SNAP. Refugees, asylum seekers, certain abused spouses and children, and certain victims of trafficking who rely upon the program for food security will be left without aid.
Governor Pritzker’s office projects that as many as 360,000 individuals will lose access to some or all SNAP benefits in Illinois. This population includes children and families that need this assistance to survive, and to be healthy and prepared to learn.
The bill also expands work requirements for SNAP recipients. The population of individuals subject to the work requirements increases from 190,000 to 450,000. This population includes former foster college students, young adults experiencing homelessness, and families with children ages 14-18.
Additional Ripple Effect: Because enrollment in SNAP qualifies families and individuals for auto-enrollment in free and reduced-price lunch programs, loss of SNAP will also complicate the ability of vulnerable families and young people to access other benefits.
Finally, let’s take a look at how the reconciliation bill will impact student loans for college and postsecondary education. The United States has a history of investing in education. We were one of the first countries to ensure public education for all students through high school, and the U.S. has worked assiduously to provide an array of loan programs designed to remove financial barriers for as many students as possible. As a result, the United States has boasted one of the most educated populations in the world — a factor unquestionably tied to the country’s strong economic presence on the world stage. OBBB represents a stark departure from this tradition. It dismantles key elements of the federal student loan system, increasing financial barriers by eliminating the Grad PLUS loan program and imposing strict annual and lifetime caps on Parent PLUS loans:
While Stafford Loans remain, their limits — $20,500 annually and $100,000 lifetime for graduate students — are insufficient to meet the full cost of education. Nearly 45,000 Illinois students benefitted from either a Parent or Grad PLUS loan during the 2023–24 fiscal year, with a total value of $1.16 billion. Parent PLUS loans, now capped at $20,000 annually and $65,000 over a student’s lifetime, will no longer fill gaps for many dependent undergraduates.
These shifts will disproportionately impact first-generation students and students of color, along with the institutions that serve them — particularly underfunded public universities like Chicago State University and Northeastern Illinois University, where Parent PLUS usage is highest. While the bill limits some forms of debt, it does so by limiting access without meaningfully improving affordability.
According to the most recent Department of Education statistics, 25.9 percent of Black students took out a Parent PLUS while pursuing a bachelor's degree, compared to 12.6 percent of White and 6.9 percent of Asian students. However, the size of the loan was smaller on average.
According to the Education Data Initiative, 40 percent of Black students take out loans for graduate school, compared to 22 percent of white students.
OBBB also eliminates all existing income-driven repayment (IDR) plans — including ICR, PAYE, REPAYE, and SAVE — and replaces them with a single, inflexible Repayment Assistance Plan (RAP). IDR plans were designed to align monthly payments with income and provide eventual forgiveness, particularly for those in public service and lower-wage sectors.
*RAP sets a $10 base monthly payment for all borrowers regardless of income, whereas previous plans did not have monthly requirements for individuals in the lowest income brackets.
*However, for those same low-income individuals, the government will ensure that the principal balance decreases by at least $50 each month. That means for borrowers making a $20 monthly payment, the government will remove an additional $30 from the principal.
*Forgiveness now takes place after 30 years of payment rather than the 20-25 years under previous plans.
Ripple Effect: Removing the previously existing protections transforms student debt into a long-term financial burden, with fewer offramps for those struggling to repay. Rather than reducing the cost of college, the bill codifies its risks—turning student loans into a tool of exclusion rather than advancement.
In Conclusion….
It is clear the changes are significant and so too will be the impact. All will affect student wellness and well-being and, in turn, academic opportunities and outcomes. As such, it is our responsibility to understand these changes and do all we can to ensure students, particularly those most reliant on public support, have what they need to learn and grow.
NEXT STEPS
Are you interested in keeping up-to-speed on federal changes in education and early care and their impact on Illinois children, students, and families? Email Jim O’Connor, Project Director, at joconnor [at] advanceillinois [dot] org for more information.
Would you be willing to share how federal changes - including cuts, rescissions, and freezes - have impacted your work or experiences in education? Complete this survey to share your story.
From the Desk—On the 2025 Spring Legislative Session
A few weeks ago, the spring 2025 session of the 104th General Assembly adjourned amid continued uncertainty about how federal changes might impact Illinois. Although there is still a great deal that we don’t know about what comes next, there are some education wins to celebrate, as well as conversations that must continue. Here, we spotlight some key outcomes and urge stakeholders to keep fighting for the education system our students deserve.
FY26 Budget Highlights
As we shared in our initial statement, this General Assembly passed a budget filled with hard choices and took efforts to protect important investments for Illinois children and students. At the same time, the state missed some critical opportunities to shore up progress. As expected, it was a challenging budget year, and increases in education spending were hard fought. That said, the addition of more than $630 million new education dollars in the FY26 budget underscores the degree to which the Governor and General Assembly value and prioritize the education and care of Illinois children and students, even when money is tight. Kudos and appreciation to every organization and individual who worked to remind our leaders about the critical importance of investing in education, including the Funding Illinois’ Future Coalition, the Minority Teachers of Illinois champions, the We, the Village Coalition, and the Coalition for Transforming Higher Education Funding. You made yourselves known, and you were heard!
The state continued to make strong investments in early childhood education and care, with an additional $250 million for programming and $7.5 million more than last year to establish the Illinois Department of Early Childhood (IDEC) as it prepares to administer programs starting in FY27. In a break with historical precedent, the state appropriated just $307 million for the Evidence-Based Funding (EBF) Formula, which is less than the minimum funding level of $350 million, but preserves the statutorily called-for $300 million increase for districts.¹ While it is good news that $300 million will go out to districts in “tier” funding, as planned and promised, the state is going to face some hard choices in the coming year, as it continues to wrestle with budget deficits and federal funding cuts and uncertainty. Because the hard reality remains: if we truly aspire to reach full funding before another generation of students graduate, we must increase the pace of investment. This is especially true given the ongoing underfunding of mandated categoricals – funding that supports required programming and costs. As proration of that funding worsens, it puts pressure on district budgets and forces them to divert other funds, like EBF, away from their intended purpose.
Higher education also faces real needs, and appropriations also broke from the norm. Specifically, FY26 appropriations to universities and community colleges were split, with some increases coming right away (1-1.5%), and additional increases (2%) held in a reserve fund for the Governor to release as needed and depending on federal actions. The total increase could be as high as 3%, if the Governor releases all the funds, but this structure both underfunds what is needed, and makes it difficult for universities and community colleges to plan for the year ahead. We both understand the pressures that may have led to this structure, but hope the Governor will promptly make clear his intention to direct the funds out, and caution the state against such measures going forward.
Legislative Highlights
The education bills that passed both houses of the General Assembly include legislation that will strengthen the educator pipeline, address barriers to learning, and improve education data infrastructure and transparency.
Successful bills that address the educator pipeline include: HB3446, which will help clarify the early childhood education coursework that counts toward credentials and degrees, and SB1947, which addresses the pipeline in several ways: adding a content test requirement for out of state applicants seeking reciprocity as they apply for Illinois educator licensure, removing content testing licensure requirements for all support personnel (such as social workers and counselors) if they already hold a professional license in their field, and introducing a process for Illinois to develop and pilot its own teacher performance assessment. In addition, SB0028 will allow each district’s joint committee to decide whether to include student growth in teacher evaluations, after a study indicated that the requirement to include a student growth component was not having the desired effect on overall evaluations. Critically, the General Assembly ensured we maintain efforts to support new teachers during their crucial first years in the classroom. As we have said consistently, there is no single solution to strengthening the educator pipeline, so we appreciate that the state continues to take a hard look at the system as a whole – from recruitment to retention – and keeps adjusting and tightening to maintain a high bar for quality, even as it expands access.
This spring, lawmakers also passed bills that remove barriers and increase access to education across the entire birth through postsecondary education continuum.
In early childhood, HB3327 will help infants born prematurely get connected to early intervention services before they even leave the hospital.
Importantly, the passage of the Safe Schools for All Act (HB3247) ensures that all students and families have access to public education regardless of immigration status and protects the integrity of the classroom environment from enforcement actions.
Generally, K-12 students are missing far too much school. SB407 establishes a Chronic Absence Task Force to study the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on chronic absenteeism and to support the development of a state strategy to help more students get back into school every day.
Access to postsecondary education remains out of reach for too many Illinoisians, so two bills address college and university access: HB3522 establishes a statewide direct admissions initiative to proactively offer college admission to Illinois high school students & community college transfer students based on GPA or credits earned, and SB1958 requires public universities to enter formal articulation agreements at the request of community colleges to promote transparency, equity, and seamless credit transfer, making it easier and faster for students to earn a bachelor’s degree after completing an associate degree.
And while it may not be as eye-catching, lawmakers also acted this spring to strengthen the state’s education data infrastructure and transparency.
SB406 establishes an Early Childhood Integrated Data System (ECIDS) to enable the newly formed Illinois Department of Early Childhood to make equity driven, inclusive, and data-informed decisions. Through this legislation, the department must also develop tools for parents and communities to access aggregated data from the ECIDS system and must ensure that the system is designed and maintained to allow for data integration and sharing with other state agencies and other entities that maintain state data.
On the other end of the education continuum, SB2039 requires Illinois Board of Higher Education (IBHE), Illinois Community College Board (ICCB), and Illinois Student Assistance Commission (ISAC) to develop a centralized, public-facing dashboard of institutional data to support better policy decisions and equity outcomes. Both of these developments are significant steps forward toward a more transparent and equitable education system in Illinois, and we can’t wait to use the dashboards and tools when they are available!
Looking Forward: There's more to do!
While there is much to celebrate, there were substantive legislative proposals that did not make it across the finish line this spring – and we look forward to continuing to work with you on these as the 104th continues in the fall and next spring.
By way of example, HB1375, a bill creating a stipend for student teachers, stalled in the Senate, after passing the House. The bill is designed to (a) provide stipends to student teachers, to reduce financial barriers into the profession, and (b) provide stipends and training to cooperating teachers to strengthen this critical role. As the state continues to grapple with ongoing shortages of fully qualified teachers, we cannot afford to miss clear opportunities to make the teaching profession more supportive, accessible, and attractive for aspiring educators.
On another front, when the Commission on Equitable Public University Funding released its recommendations for advancing a healthier, more accessible public university system last spring, Senate Majority Leader Kimberly Lightford and Representative Carol Ammons got to work. The Adequate and Equitable Public University Funding bill, which provides increased state funding for all Illinois public universities and directs state funds most heavily to the universities furthest from adequacy, was formally introduced this spring, and with considerable collaboration by universities and communities, gained significant traction across the state. While lawmakers have not yet taken action to adopt the funding formula, we cannot ‘unlearn’ what we now know: (1) that many of our public universities are woefully underfunded, lacking the resources they need to ensure all students earn degrees, and (2) that some institutions are in much worse financial position than others. We cannot keep doing what we have been doing, so it is powerful that we have found a better way — one that will result in more than 122,000 additional graduates contributing to our local and state prosperity and progress, once the bill is passed and fully funded. It is time to make this a reality.
With higher education under significant new pressure at the federal level, it is critical that the state act to support our community colleges and universities. We appreciate that this session provided multiple opportunities to reimagine the postsecondary landscape, be it through funding reform, stronger articulation and enrollment, or targeted strategies to create baccalaureate pathways via community colleges. The time for action is now.
Conclusion
Despite very real budget challenges and federal uncertainty, Illinois took some important actions this spring. That said, we are not done. Looking ahead, even more will be required as we learn how changes in Washington, DC will impact Illinois – fiscally and otherwise. In every challenge there is opportunity, and ours is this: We can and must work together to ensure that all students and their families are safe, supported, and have access to a strong and healthy education system. Let us take this moment to re-commit ourselves to the work ahead – it has never been more important.
In partnership,
Robin
The $43 million reduction came out of dollars that otherwise would have funded the FY26 Property Tax Relief Grant fund, a program that encourages and supports communities to lower property taxes by replacing lost property tax revenue (due to reductions) with state funding.